
 Ancient Roman Baths
Ancient Roman Baths
Bathing played a major part in ancient Roman culture and society. Bathing was one of the most common daily activities in Roman culture, and was practiced across a wide variety of social classes. Though many contemporary cultures see bathing as a very private activity conducted in the home, bathing in Rome was a communal activity.
Bathing in Greek and Roman Times
Some of the earliest descriptions of western bathing practices came from Greece. The Greeks began bathing regimens that formed the foundation for modern spa procedures. These Aegean people utilized small bathtubs, wash basins, and foot baths for personal cleanliness. The earliest such findings are the baths in the palace complex at Knossos, Crete, and the luxurious alabaster bathtubs excavated in Akrotiri, Santorini; both date from the mid-2nd millennium BC. They established public baths and showers within their gymnasium complexes for relaxation and personal hygiene.
 Greek mythology specified that certain natural springs or tidal pools were blessed by the gods to cure disease. Around these sacred pools, Greeks established bathing facilities for those desiring healing. Supplicants left offerings to the gods for healing at these sites and bathed themselves in hopes of a cure. The Spartans developed a primitive vapor bath.
Greek mythology specified that certain natural springs or tidal pools were blessed by the gods to cure disease. Around these sacred pools, Greeks established bathing facilities for those desiring healing. Supplicants left offerings to the gods for healing at these sites and bathed themselves in hopes of a cure. The Spartans developed a primitive vapor bath.
At Serangeum, an early Greek balneum (bathhouse, loosely translated), bathing chambers were cut into the hillside from which the hot springs issued. A series of niches cut into the rock above the chambers held bathers' clothing. One of the bathing chambers had a decorative mosaic floor depicting a driver and chariot pulled by four horses, a woman followed by two dogs, and a dolphin below. Thus, the early Greeks used the natural features, but expanded them and added their own amenities, such as decorations and shelves. During later Greek civilization, bathhouses were often built in conjunction with athletic fields.
The Romans emulated many of the Greeks bathing practices, Romans surpassed the Greeks in the size of their baths. As in Greece, the Roman bath became a focal center for social and recreational activity. As the Roman Empire expanded, the idea of the public bath spread to all parts of the Mediterranean and into regions of Europe and North Africa. With the construction of the aqueducts, the Romans had enough water not only for domestic, agricultural, and industrial uses, but also for their leisurely pursuits. The aqueducts provided water that was later heated for use in the baths. Today, the extent of the Roman bath is revealed at ruins and in archaeological excavations in Europe, Africa, and the Middle East.
With the construction of the aqueducts, the Romans had enough water not only for domestic, agricultural, and industrial uses, but also for their leisurely pursuits. The aqueducts provided water that was later heated for use in the baths. Today, the extent of the Roman bath is revealed at ruins and in archaeological excavations in Europe, Africa, and the Middle East.
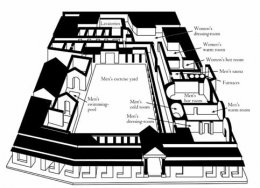
These Roman baths varied from simple to exceedingly elaborate structures, and they varied in size, arrangement, and decoration. In taking a Roman bath, the bather induced sweating by gradually exposing himself to increasing temperatures. To accommodate this ritual, all Roman bathhouses contained a series of rooms which got progressively hotter. Most contained an apodyterium - a room just inside the entrance where the bather stored his clothes. Next, the bather progressed into the frigidarium (cold room) with its tank of cold water, the tepidarium (warm room), and finally the caldarium (hot room). The caldarium, heated by a brazier underneath the hollow floor, contained cold-water basins which the bather could use for cooling. After taking this series of sweat and/or immersion baths, the bather returned to the cooler tepidarium for a massage with oils and final scraping with metal implements. Some baths also contained a laconium (a dry, resting room) where the bather completed the process by resting and sweating.
The caldarium, heated by a brazier underneath the hollow floor, contained cold-water basins which the bather could use for cooling. After taking this series of sweat and/or immersion baths, the bather returned to the cooler tepidarium for a massage with oils and final scraping with metal implements. Some baths also contained a laconium (a dry, resting room) where the bather completed the process by resting and sweating.
The layout of Roman baths contained other architectural features of note. Because wealthy Romans brought slaves to attend to their bathing needs, the bathhouse usually had three entrances: one for men, one for women, and one for slaves. The preference of symmetry in Roman architecture usually meant a symmetrical facade, even though the women's area was usually smaller than the men's area because of fewer numbers of patrons. Usually solid walls or placement on opposite sides of the building separated the men's and women's sections. Roman bathhouses often contained a courtyard, or Palaestra, which was an open-air garden used for exercise. In some cases the builders made the palestra an interior courtyard, and in other cases the builders placed the palestra in front of the bathhouse proper and incorporated it into the formal approach. Sometimes the palestra held a swimming pool. Most often a colonnade outlined the palestra's edges.
Republican bathhouses often had separate bathing facilities for women and men, but by the 1st century AD mixed bathing was common and is a practice frequently referred to in Martial and Juvenal, as well as in Pliny and Quintilian. However, gender separation was restored by Emperor Hadrian.




RELATED VIDEO












