
The Colosseum was built of blocks of travertine stone extracted from the quarries of Albulae near Tivoli and brought to Rome by a wide road specially constructed for the purpose. The amphitheater forms an oval 527 meters ( 1, 729) in circumference with diameters of 189 and 156 meters (615 and 510 ft). The height of the four-storied wall is 48 meters (157 ft).
The Colosseum contained 45, 000 sitting places and 5, 000 standing places. The broad paved circular piazza that surrounded the amphitheater allowed easy access to every part of the façade. There were 80 entrance arches, of these the four at the extremities of the major and minor axes were forbidden to the public and not numbered. The major axis entrances gave direct unrestricted access to the arena itself. In contrast both of the minor axis entrances gave direct access to special reserved boxes.
Seating
The first tier of the seating began four meters above the arena with the Podium. It was reserved for the most important Romans, namely the Emperor, the Vestal Virgins, the priests and the senators. The Emperor and his court reclined in the imperial box on the northern side of the arena. The empress and her female entourage occupied the box opposite of the emperor. These two locations were the best seats to occupy in order to see and be seen.
Above the podium were the tiers for the ordinary public. The noble class and knights sat in the first 14 rows of the Colosseum, the section known as the ima cavea. Roman citizens sat in the next block of seats, that is the media cavea. The rest of the population including the urban poor, foreigners, freed slaves and other slaves were lumped together in the highest block of seats, the summa cavea. Finally, women, presumably the respectable wives and daughter of Roman citizens, were expected to sit under the protecting shelter of the colonnade that usually crowned the theater seating area.
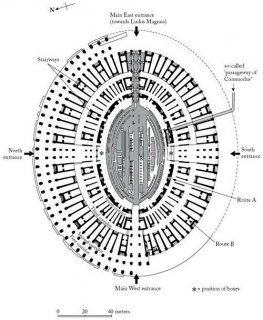
Hypogeum
Under the arena was the hypogeum ( literally underground), a vast network of tunnels and passages as well as chambers for the gladiators, animals, slaves. It contained lifts operated by ropes and pulleys which led directly to the arena through the trap doors.
RELATED VIDEO




 Giovanni Battista (also Giambattista) Piranesi (4 October 1720 – 9 November 1778) was an Italian artist famous for his etchings of Rome and of fictitious and atmospheric "prisons" (Carceri d'Invenzione).
Giovanni Battista (also Giambattista) Piranesi (4 October 1720 – 9 November 1778) was an Italian artist famous for his etchings of Rome and of fictitious and atmospheric "prisons" (Carceri d'Invenzione).







